Introduction to Networks (Version 7.00) – Final Exam Answers Full
1. What two ICMPv6 message types must be permitted through IPv6 access control lists to allow resolution of Layer 3 addresses to Layer 2 MAC addresses? (Choose two.)
- neighbor solicitations
- echo requests
- neighbor advertisements
- echo replies
- router solicitations
- router advertisements
2. Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FEC0::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FE80::/10
- FF00::/8
3. What would be the interface ID of an IPv6 enabled interface with a MAC address of 1C-6F-65-C2-BD-F8 when the interface ID is generated by using the EUI-64 process?
- 0C6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 1E6F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- C16F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
- 106F:65FF:FEC2:BDF8
4. An organization is assigned an IPv6 address block of 2001:db8:0:ca00::/56. How many subnets can be created without using bits in the interface ID space?
- 256
- 512
- 1024
- 4096
5. Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?

- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- 172.168.10.99
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- 172.168.10.65
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
6. When a switch configuration includes a user-defined error threshold on a per-port basis, to which switching method will the switch revert when the error threshold is reached?
- cut-through
- store-and-forward
- fast-forward
- fragment-free
7. Which two statements are correct about MAC and IP addresses during data transmission if NAT is not involved? (Choose two.)
- Destination IP addresses in a packet header remain constant along the entire path to a target host.
- Destination MAC addresses will never change in a frame that goes across seven routers.
- Every time a frame is encapsulated with a new destination MAC address, a new destination IP address is needed.
- Destination and source MAC addresses have local significance and change every time a frame goes from one LAN to another.
- A packet that has crossed four routers has changed the destination IP address four times.
8. What is one main characteristic of the data link layer?
- It generates the electrical or optical signals that represent the 1 and 0 on the media.
- It converts a stream of data bits into a predefined code.
- It shields the upper layer protocol from being aware of the physical medium to be used in the communication.
- It accepts Layer 3 packets and decides the path by which to forward the packet to a remote network.
9. What are three characteristics of the CSMA/CD process? (Choose three.)
- The device with the electronic token is the only one that can transmit after a collision.
- A device listens and waits until the media is not busy before transmitting.
- After detecting a collision, hosts can attempt to resume transmission after a random time delay has expired.
- All of the devices on a segment see data that passes on the network medium.
- A jam signal indicates that the collision has cleared and the media is not busy.
- Devices can be configured with a higher transmission priority.
10. What are two primary responsibilities of the Ethernet MAC sublayer? (Choose two.)
- error detection
- frame delimiting
- accessing the media
- data encapsulation
- logical addressing
11. Which two commands can be used on a Windows host to display the routing table? (Choose two.)
- netstat -s
- route print
- show ip route
- netstat -r
- tracert
12. What are two functions that are provided by the network layer? (Choose two.)
- directing data packets to destination hosts on other networks
- placing data on the network medium
- carrying data between processes that are running on source and destination hosts
- providing dedicated end-to-end connections
- providing end devices with a unique network identifier
13. Which two statements describe features of an IPv4 routing table on a router? (Choose two.)
- Directly connected interfaces will have two route source codes in the routing table: C and S.
- If there are two or more possible routes to the same destination, the route associated with the higher metric value is included in the routing table.
- The netstat -r command can be used to display the routing table of a router.
- The routing table lists the MAC addresses of each active interface.
- It stores information about routes derived from the active router interfaces.
- If a default static route is configured in the router, an entry will be included in the routing table with source code S.
14. How does the service password-encryption command enhance password security on Cisco routers and switches?
- It requires encrypted passwords to be used when connecting remotely to a router or switch with Telnet.
- It encrypts passwords that are stored in router or switch configuration files.
- It requires that a user type encrypted passwords to gain console access to a router or switch.
- It encrypts passwords as they are sent across the network.
15. Why would a Layer 2 switch need an IP address?
- to enable the switch to send broadcast frames to attached PCs
- to enable the switch to function as a default gateway
- to enable the switch to be managed remotely
- to enable the switch to receive frames from attached PCs
16. What characteristic describes identity theft?
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
- software that identifies fast-spreading threats
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
17. Match each description to its corresponding term. (Not all options are used.)


18. A user sends an HTTP request to a web server on a remote network. During encapsulation for this request, what information is added to the address field of a frame to indicate the destination?
- the network domain of the destination host
- the IP address of the default gateway
- the MAC address of the destination host
- the MAC address of the default gateway
19. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function of TCP or UDP in this situation? (Choose three.)
- The source port field identifies the running application or service that will handle data returning to the PC.
- The TCP process running on the PC randomly selects the destination port when establishing a session with the server.
- UDP segments are encapsulated within IP packets for transport across the network.
- The UDP destination port number identifies the application or service on the server which will handle the data.
- TCP is the preferred protocol when a function requires lower network overhead.
- The TCP source port number identifies the sending host on the network.
20. Match each description with the corresponding TCP mechanism. (Not all options are used.)

21. Refer to the exhibit. Which two network addresses can be assigned to the network containing 10 hosts? Your answers should waste the fewest addresses, not reuse addresses that are already assigned, and stay within the 10.18.10.0/24 range of addresses. (Choose two.)

- 10.18.10.200/28
- 10.18.10.208/28
- 10.18.10.240/27
- 10.18.10.200/27
- 10.18.10.224/27
- 10.18.10.224/28
22. Refer to the exhibit. A company uses the address block of 128.107.0.0/16 for its network. What subnet mask would provide the maximum number of equal size subnets while providing enough host addresses for each subnet in the exhibit?

- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.224
23. A network administrator wants to have the same subnet mask for three subnetworks at a small site. The site has the following networks and numbers of devices:
Subnetwork A: IP phones – 10 addresses Subnetwork B: PCs – 8 addresses Subnetwork C: Printers – 2 addresses
What single subnet mask would be appropriate to use for the three subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.252
24. Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)

25. What two pieces of information are displayed in the output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose two.)
- IP addresses
- interface descriptions
- MAC addresses
- next-hop addresses
- Layer 1 statuses
- speed and duplex settings
26. A user is complaining that an external web page is taking longer than normal to load.The web page does eventually load on the user machine. Which tool should the technician use with administrator privileges in order to locate where the issue is in the network?
- ping
- nslookup
- tracert
- ipconfig /displaydns
27. A network technician is researching the use of fiber optic cabling in a new technology center. Which two issues should be considered before implementing fiber optic media? (Choose two.)
- Fiber optic cabling requires different termination and splicing expertise from what copper cabling requires.
- Fiber optic cabling requires specific grounding to be immune to EMI.
- Fiber optic cabling is susceptible to loss of signal due to RFI.
- Fiber optic cable is able to withstand rough handling.
- Fiber optic provides higher data capacity but is more expensive than copper cabling.
28. What technique is used with UTP cable to help protect against signal interference from crosstalk?
- wrapping a foil shield around the wire pairs
- twisting the wires together into pairs
- terminating the cable with special grounded connectors
- encasing the cables within a flexible plastic sheath
29. A network administrator is designing the layout of a new wireless network. Which three areas of concern should be accounted for when building a wireless network? (Choose three.)
- extensive cabling
- mobility options
- packet collision
- interference
- security
- coverage area
30. Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)

31. Users report that the network access is slow. After questioning the employees, the network administrator learned that one employee downloaded a third-party scanning program for the printer. What type of malware might be introduced that causes slow performance of the network?
- virus
- worm
- phishing
- spam
32. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
33.Refer to the exhibit. Host B on subnet Teachers transmits a packet to host D on subnet Students. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 addresses are contained in the PDUs that are transmitted from host B to the router?

Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-dd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-cd
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.99
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.99
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.10.200
Layer 2 destination address = 00-00-0c-94-36-ab
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.100.200
Layer 2 source address = 00-00-0c-94-36-bb
Layer 3 destination address = 172.16.20.200
Layer 3 source address = 172.16.100.200
34. What does the term “attenuation” mean in data communication?
- strengthening of a signal by a networking device
- leakage of signals from one cable pair to another
- time for a signal to reach its destination
- loss of signal strength as distance increases
35. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message that is displayed in the exhibit. What is the problem?

- The entire command, configure terminal, must be used.
- The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.
- The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
36. Which two protocols operate at the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol suite? (Choose two.)
- TCP
- IP
- UDP
- POP
- DNS
- Ethernet
37. A company has a file server that shares a folder named Public. The network security policy specifies that the Public folder is assigned Read-Only rights to anyone who can log into the server while the Edit rights are assigned only to the network admin group. Which component is addressed in the AAA network service framework?
- automation
- accounting
- authentication
- authorization
38. What three requirements are defined by the protocols used in network communcations to allow message transmission across a network? (Choose three.)
- message size
- message encoding
- connector specifications
- media selection
- delivery options
- end-device installation
39. What are two characteristics of IP? (Choose two.)
- does not require a dedicated end-to-end connection
- operates independently of the network media
- retransmits packets if errors occur
- re-assembles out of order packets into the correct order at the receiver end
- guarantees delivery of packets
40. An employee of a large corporation remotely logs into the company using the appropriate username and password. The employee is attending an important video conference with a customer concerning a large sale. It is important for the video quality to be excellent during the meeting. The employee is unaware that after a successful login, the connection to the company ISP failed. The secondary connection, however, activated within seconds. The disruption was not noticed by the employee or other employees.
What three network characteristics are described in this scenario? (Choose three.)
- security
- quality of service
- scalability
- powerline networking
- integrity
- fault tolerance
41. What are two common causes of signal degradation when using UTP cabling? (Choose two.)
- improper termination
- low-quality shielding in cable
- installing cables in conduit
- low-quality cable or connectors
- loss of light over long distances
42. Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
43. Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)

- This host does not have a default gateway configured.
- There are 4 hops between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
44. Which two statements describe how to assess traffic flow patterns and network traffic types using a protocol analyzer? (Choose two.)
- Capture traffic on the weekends when most employees are off work.
- Capture traffic during peak utilization times to get a good representation of the different traffic types.
- Only capture traffic in the areas of the network that receive most of the traffic such as the data center.
- Perform the capture on different network segments.
- Only capture WAN traffic because traffic to the web is responsible for the largest amount of traffic on a network.
45. What is the consequence of configuring a router with the ipv6 unicast-routing global configuration command?
- All router interfaces will be automatically activated.
- The IPv6 enabled router interfaces begin sending ICMPv6 Router Advertisement messages.
- Each router interface will generate an IPv6 link-local address.
- It statically creates a global unicast address on this router.
46. Which three layers of the OSI model map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- application
- network
- data link
- session
- presentation
- transport
47. Refer to the exhibit. If PC1 is sending a packet to PC2 and routing has been configured between the two routers, what will R1 do with the Ethernet frame header attached by PC1?

- nothing, because the router has a route to the destination network
- open the header and use it to determine whether the data is to be sent out S0/0/0
- open the header and replace the destination MAC address with a new one
- remove the Ethernet header and configure a new Layer 2 header before sending it out S0/0/0
48. What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
49. What are two features of ARP? (Choose two.)
- When a host is encapsulating a packet into a frame, it refers to the MAC address table to determine the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses.
- An ARP request is sent to all devices on the Ethernet LAN and contains the IP address of the destination host and its multicast MAC address.
- If a host is ready to send a packet to a local destination device and it has the IP address but not the MAC address of the destination, it generates an ARP broadcast.
- If no device responds to the ARP request, then the originating node will broadcast the data packet to all devices on the network segment.
- If a device receiving an ARP request has the destination IPv4 address, it responds with an ARP reply.
50. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 90 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.224
51. What are two ICMPv6 messages that are not present in ICMP for IPv4? (Choose two.)
- Neighbor Solicitation
- Destination Unreachable
- Host Confirmation
- Time Exceeded
- Router Advertisement
- Route Redirection
52. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 80. What service is the client requesting?
- DHCP
- SMTP
- DNS
- HTTP
53. What is an advantage for small organizations of adopting IMAP instead of POP?
- POP only allows the client to store messages in a centralized way, while IMAP allows distributed storage.
- Messages are kept in the mail servers until they are manually deleted from the email client.
- When the user connects to a POP server, copies of the messages are kept in the mail server for a short time, but IMAP keeps them for a long time.
- IMAP sends and retrieves email, but POP only retrieves email.
54. A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- ipconfig
- netstat
- nslookup
55. Which two functions are performed at the LLC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
- implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- implements a process to delimit fields within an Ethernet 2 frame
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
56. The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
57. What happens when the transport input ssh command is entered on the switch vty lines?
- The SSH client on the switch is enabled.
- The switch requires a username/password combination for remote access.
- Communication between the switch and remote users is encrypted.
- The switch requires remote connections via a proprietary client software.
58. Match the type of threat with the cause. (Not all options are used.)
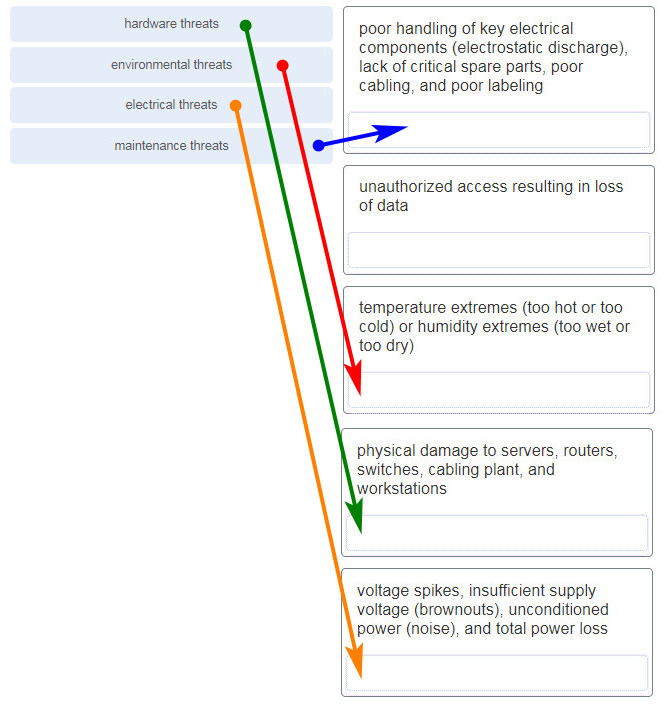
59. A disgruntled employee is using some free wireless networking tools to determine information about the enterprise wireless networks. This person is planning on using this information to hack the wireless network. What type of attack is this?
- DoS
- access
- reconnaissance
- Trojan horse
60. What service is provided by HTTP?
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
61. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 67. What service is the client requesting?
- FTP
- DHCP
- Telnet
- SSH
62. What are two problems that can be caused by a large number of ARP request and reply messages? (Choose two.)
- Switches become overloaded because they concentrate all the traffic from the attached subnets.
- The ARP request is sent as a broadcast, and will flood the entire subnet.
- The network may become overloaded because ARP reply messages have a very large payload due to the 48-bit MAC address and 32-bit IP address that they contain.
- A large number of ARP request and reply messages may slow down the switching process, leading the switch to make many changes in its MAC table.
- All ARP request messages must be processed by all nodes on the local network.
63. A group of Windows PCs in a new subnet has been added to an Ethernet network. When testing the connectivity, a technician finds that these PCs can access local network resources but not the Internet resources. To troubleshoot the problem, the technician wants to initially confirm the IP address and DNS configurations on the PCs, and also verify connectivity to the local router. Which three Windows CLI commands and utilities will provide the necessary information? (Choose three.)
- netsh interface ipv6 show neighbor
- arp -a
- tracert
- ping
- ipconfig
- nslookup
- telnet
64. During the process of forwarding traffic, what will the router do immediately after matching the destination IP address to a network on a directly connected routing table entry?
- analyze the destination IP address
- switch the packet to the directly connected interface
- look up the next-hop address for the packet
- discard the traffic after consulting the route table
65. What characteristic describes antispyware?
- applications that protect end devices from becoming infected with malicious software
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
66. A network administrator needs to keep the user ID, password, and session contents private when establishing remote CLI connectivity with a switch to manage it. Which access method should be chosen?
- Telnet
- AUX
- SSH
- Console
67. What are the two most effective ways to defend against malware? (Choose two.)
- Implement a VPN.
- Implement network firewalls.
- Implement RAID.
- Implement strong passwords.
- Update the operating system and other application software.
- Install and update antivirus software.
68. Which type of security threat would be responsible if a spreadsheet add-on disables the local software firewall?
- brute-force attack
- Trojan horse
- DoS
- buffer overflow
69. Match the header field with the appropriate layer of the OSI model. (Not all options are used.)
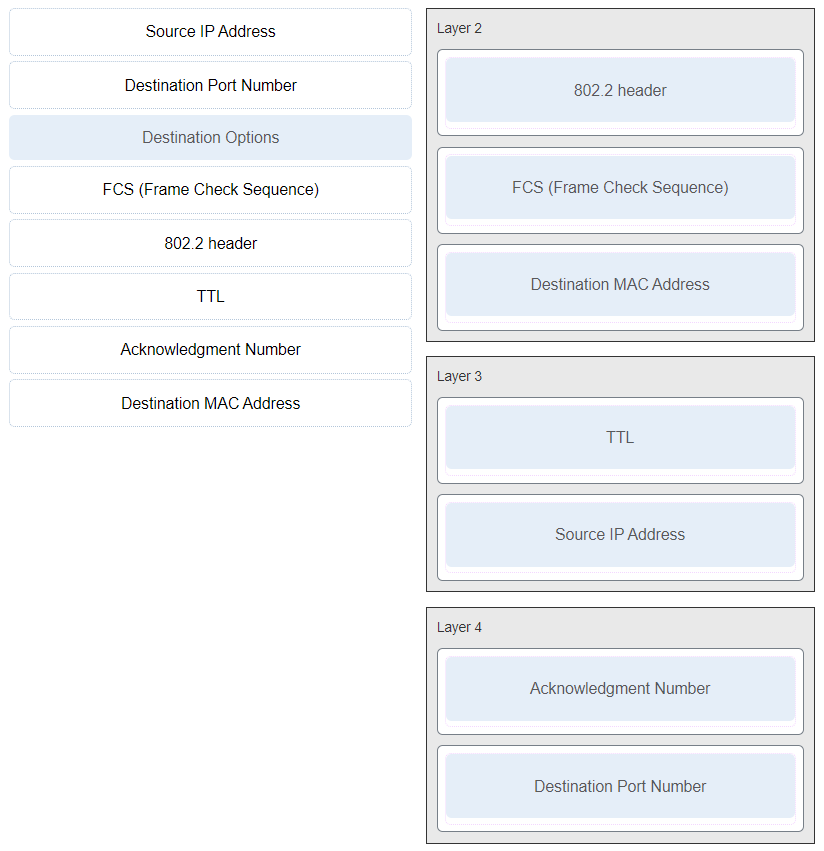

70. Which frame field is created by a source node and used by a destination node to ensure that a transmitted data signal has not been altered by interference, distortion, or signal loss?
- User Datagram Protocol field
- transport layer error check field
- flow control field
- frame check sequence field
- error correction process field
71. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 4 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192
72. What service is provided by POP3?
- Retrieves email from the server by downloading the email to the local mail application of the client.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
73. What two security solutions are most likely to be used only in a corporate environment? (Choose two.)
- antispyware
- virtual private networks
- intrusion prevention systems
- strong passwords
- antivirus software
74. What characteristic describes antivirus software?
- applications that protect end devices from becoming infected with malicious software
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
75. What mechanism is used by a router to prevent a received IPv4 packet from traveling endlessly on a network?
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It checks the value of the TTL field and if it is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Destination Unreachable message to the source host.
- It decrements the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 0, it discards the packet and sends a Time Exceeded message to the source host.
- It increments the value of the TTL field by 1 and if the result is 100, it discards the packet and sends a Parameter Problem message to the source host.
76. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 69. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- DHCP
- SMTP
- TFTP
77. An administrator defined a local user account with a secret password on router R1 for use with SSH. Which three additional steps are required to configure R1 to accept only encrypted SSH connections? (Choose three.)
- Configure DNS on the router.
- Generate two-way pre-shared keys.
- Configure the IP domain name on the router.
- Generate the SSH keys.
- Enable inbound vty SSH sessions.
- Enable inbound vty Telnet sessions.
78. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication? (Choose two.)
- places information in the Ethernet frame that identifies which network layer protocol is being encapsulated by the frame
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- responsible for internal structure of Ethernet frame
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
- implements trailer with frame check sequence for error detection
79. An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::2. What is the target of this packet?
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link
- all IPv6 DHCP servers
- all IPv6 enabled devices across the network
- all IPv6 configured routers on the local link
80. What are the three parts of an IPv6 global unicast address? (Choose three.)
- subnet ID
- subnet mask
- broadcast address
- global routing prefix
- interface ID
81. A client is using SLAAC to obtain an IPv6 address for its interface. After an address has been generated and applied to the interface, what must the client do before it can begin to use this IPv6 address?
- It must send a DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST message to request the address of the DNS server.
- It must send a DHCPv6 REQUEST message to the DHCPv6 server to request permission to use this address.
- It must send an ICMPv6 Router Solicitation message to determine what default gateway it should use.
- It must send an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message to ensure that the address is not already in use on the network.
82. A new network administrator has been asked to enter a banner message on a Cisco device. What is the fastest way a network administrator could test whether the banner is properly configured?
- Enter CTRL-Z at the privileged mode prompt.
- Exit global configuration mode.
- Power cycle the device.
- Reboot the device.
- Exit privileged EXEC mode and press Enter .
83. What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- token passing
- CSMA/CA
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CD
84. What is a function of the data link layer?
- provides the formatting of data
- provides end-to-end delivery of data between hosts
- provides delivery of data between two applications
- provides for the exchange of frames over a common local media
85. What is the purpose of the TCP sliding window?
- to ensure that segments arrive in order at the destination
- to end communication when data transmission is complete
- to inform a source to retransmit data from a specific point forward
- to request that a source decrease the rate at which it transmits data
86. What characteristic describes spyware?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
87. Which switching method drops frames that fail the FCS check?
- store-and-forward switching
- borderless switching
- ingress port buffering
- cut-through switching
88. Two pings were issued from a host on a local network. The first ping was issued to the IP address of the default gateway of the host and it failed. The second ping was issued to the IP address of a host outside the local network and it was successful. What is a possible cause for the failed ping?
- The default gateway is not operational.
- The default gateway device is configured with the wrong IP address.
- Security rules are applied to the default gateway device, preventing it from processing ping requests.
- The TCP/IP stack on the default gateway is not working properly.
89. What service is provided by FTP?
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
90. A user is attempting to access http://www.cisco.com/ without success. Which two configuration values must be set on the host to allow this access? (Choose two.)
- DNS server
- source port number
- HTTP server
- source MAC address
- default gateway
91. Which two statements accurately describe an advantage or a disadvantage when deploying NAT for IPv4 in a network? (Choose two.)
- NAT adds authentication capability to IPv4.
- NAT introduces problems for some applications that require end-to-end connectivity.
- NAT will impact negatively on switch performance.
- NAT provides a solution to slow down the IPv4 address depletion.
- NAT improves packet handling.
- NAT causes routing tables to include more information.
92. What subnet mask is needed if an IPv4 network has 40 devices that need IP addresses and address space is not to be wasted?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.224
93. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 issues an ARP request because it needs to send a packet to PC2. In this scenario, what will happen next?
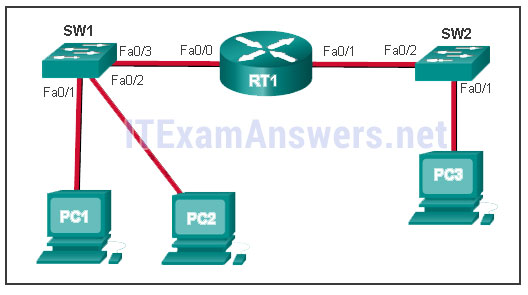

- PC2 will send an ARP reply with its MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/0 MAC address.
- RT1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with the PC2 MAC address.
- SW1 will send an ARP reply with its Fa0/1 MAC address.
94. What service is provided by BOOTP?
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- Legacy application that enables a diskless workstation to discover its own IP address and find a BOOTP server on the network.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
95. What characteristic describes adware?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- software that is installed on a user device and collects information about the user
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
96. What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
97. Match a statement to the related network model. (Not all options are used.)
- requires a specific user interface
- no dedicated server is required
- a background service is required
- client and server roles are set on a per request basis
- devices can only function in one role at a time
Answer:
peer-to-peer network
peer-to-peer network
- no dedicated server is required
- client and server roles are set on a per request basis
peer-to-peer application
- requires a specific user interface
- a background service is required
98. Which information does the show startup-config command display?
- the IOS image copied into RAM
- the bootstrap program in the ROM
- the contents of the current running configuration file in the RAM
- the contents of the saved configuration file in the NVRAM
99. Refer to the exhibit. What three facts can be determined from the viewable output of the show ip interface brief command? (Choose three.)
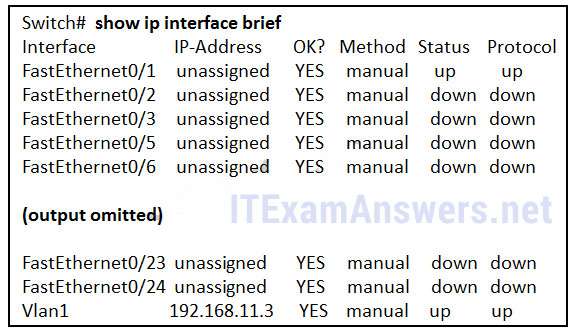

- Two physical interfaces have been configured.
- The switch can be remotely managed.
- One device is attached to a physical interface.
- Passwords have been configured on the switch.
- Two devices are attached to the switch.
- The default SVI has been configured.
100. Match each type of frame field to its function. (Not all options are used.)


101. What is the subnet ID associated with the IPv6 address 2001:DA48:FC5:A4:3D1B::1/64?
- 2001:DA48::/64
- 2001:DA48:FC5::A4:/64
- 2001:DA48:FC5:A4::/64
- 2001::/64
102. Match the firewall function to the type of threat protection it provides to the network. (Not all options are used.)
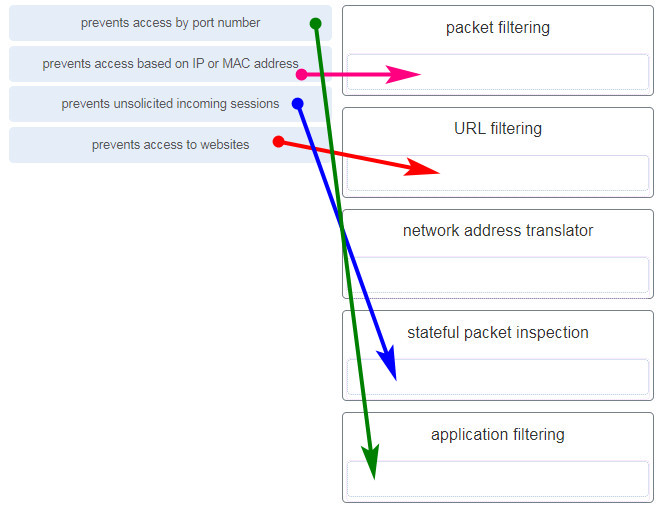

- packet filtering – prevents access based on IP or MAC address
- URL filtering – prevents access to websites
- network address translator – (none)
- stateful packet inspection – prevents unsolicited incoming sessions
- application filtering – prevents access by port number
103. Users are reporting longer delays in authentication and in accessing network resources during certain time periods of the week. What kind of information should network engineers check to find out if this situation is part of a normal network behavior?
- syslog records and messages
- the network performance baseline
- debug output and packet captures
- network configuration files
104. What characteristic describes a VPN?
- software on a router that filters traffic based on IP addresses or applications
- software that identifies fast-spreading threats
- a tunneling protocol that provides remote users with secure access into the network of an organization
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
105. Which two statements are correct in a comparison of IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers? (Choose two.)
- The Source Address field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
- The Version field from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6.
- The Destination Address field is new in IPv6.
- The Header Checksum field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
- The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6.
106. A network administrator wants to have the same network mask for all networks at a particular small site. The site has the following networks and number of devices:
IP phones – 22 addresses
PCs – 20 addresses needed
Printers – 2 addresses needed
Scanners – 2 addresses needed
IP phones – 22 addresses
PCs – 20 addresses needed
Printers – 2 addresses needed
Scanners – 2 addresses needed
The network administrator has deemed that 192.168.10.0/24 is to be the network used at this site. Which single subnet mask would make the most efficient use of the available addresses to use for the four subnetworks?
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.252
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.224
107. What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- A company can monopolize the market.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.
108. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 200 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.224
109. What are three commonly followed standards for constructing and installing cabling? (Choose three.)
- cost per meter (foot)
- cable lengths
- connector color
- pinouts
- connector types
- tensile strength of plastic insulator
110. Refer to the exhibit. What is wrong with the displayed termination?

- The woven copper braid should not have been removed.
- The wrong type of connector is being used.
- The untwisted length of each wire is too long.
- The wires are too thick for the connector that is used.
111. Match the characteristic to the category. (Not all options are used.)
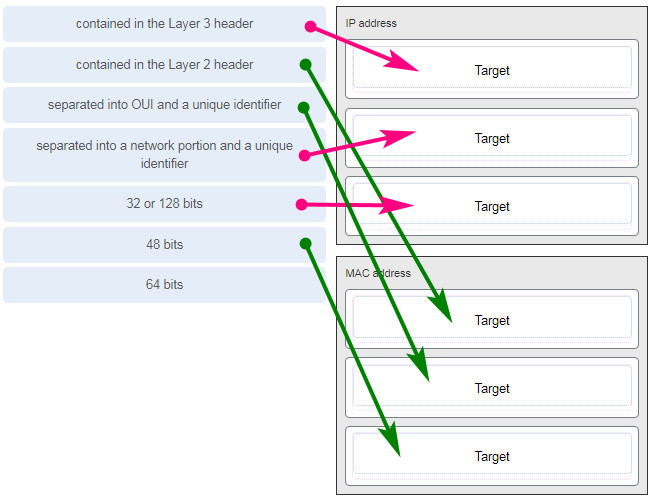

112. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 143. What service is the client requesting?
- IMAP
- FTP
- SSH
- Telnet
113. What are two characteristics shared by TCP and UDP? (Choose two.)
- default window size
- connectionless communication
- port numbering
- 3-way handshake
- ability to to carry digitized voice
- use of checksum
114. Which value, that is contained in an IPv4 header field, is decremented by each router that receives a packet?
- Header Length
- Differentiated Services
- Time-to-Live
- Fragment Offset
115. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 21. What service is the client requesting?
- FTP
- LDAP
- SLP
- SNMP
116. What attribute of a NIC would place it at the data link layer of the OSI model?
- attached Ethernet cable
- IP address
- MAC address
- RJ-45 port
- TCP/IP protocol stack
117. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 10 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.192
- 255.255.255.248
- 255.255.255.224
118. A user is executing a tracert to a remote device. At what point would a router, which is in the path to the destination device, stop forwarding the packet?
- when the router receives an ICMP Time Exceeded message
- when the RTT value reaches zero
- when the host responds with an ICMP Echo Reply message
- when the value in the TTL field reaches zero
- when the values of both the Echo Request and Echo Reply messages reach zero
119. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has assigned the LAN of LBMISS an address range of 192.168.10.0. This address range has been subnetted using a /29 prefix. In order to accommodate a new building, the technician has decided to use the fifth subnet for configuring the new network (subnet zero is the first subnet). By company policies, the router interface is always assigned the first usable host address and the workgroup server is given the last usable host address. Which configuration should be entered into the properties of the workgroup server to allow connectivity to the Internet?
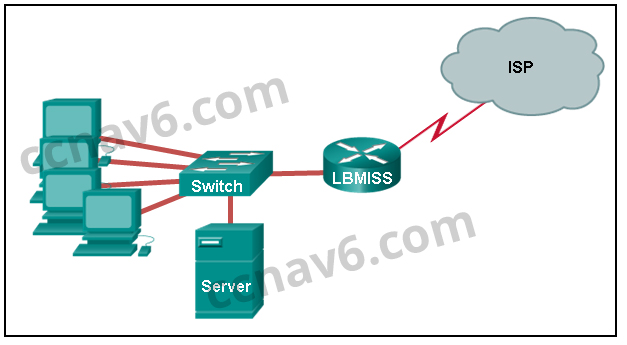

- IP address: 192.168.10.65 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.76
- IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.240, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
- IP address: 192.168.10.38 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.33
- IP address: 192.168.10.41 subnet mask: 255.255.255.248, default gateway: 192.168.10.46
- IP address: 192.168.10.254 subnet mask: 255.255.255.0, default gateway: 192.168.10.1
120. Refer to the exhibit. The switches are in their default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for its default gateway. Which network hosts will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
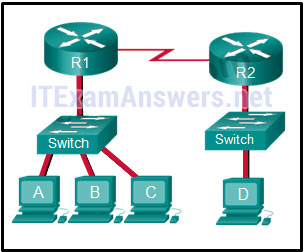

- only host D
- only router R1
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only hosts A, B, C, and D
- only hosts B and C
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
121. Which two traffic types use the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP)? (Choose two.)
- video
- web
- file transfer
- voice
- peer to peer
122. Which wireless technology has low-power and data rate requirements making it popular in home automation applications?
- ZigBee
- LoRaWAN
- 5G
- Wi-Fi
123. Which layer of the TCP/IP model provides a route to forward messages through an internetwork?
- application
- network access
- internet
- transport
124. Which type of server relies on record types such as A, NS, AAAA, and MX in order to provide services?
- DNS
- file
- web
125. What are proprietary protocols?
- protocols developed by private organizations to operate on any vendor hardware
- protocols that can be freely used by any organization or vendor
- protocols developed by organizations who have control over their definition and operation
- a collection of protocols known as the TCP/IP protocol suite
126. What service is provided by DNS?
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- A basic set of rules for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files on the web.
- Allows for data transfers between a client and a file server.
- Uses encryption to secure the exchange of text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
127. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 110. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- DHCP
- SMTP
- POP3
128. What command can be used on a Windows PC to see the IP configuration of that computer?
- show ip interface brief
- ping
- show interfaces
- ipconfig
129. A wired laser printer is attached to a home computer. That printer has been shared so that other computers on the home network can also use the printer. What networking model is in use?
- client-based
- master-slave
- point-to-point
- peer-to-peer (P2P)
130. What characteristic describes a virus?
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- malicious software or code running on an end device
131. Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
132. Match the description to the IPv6 addressing component. (Not all options are used.)
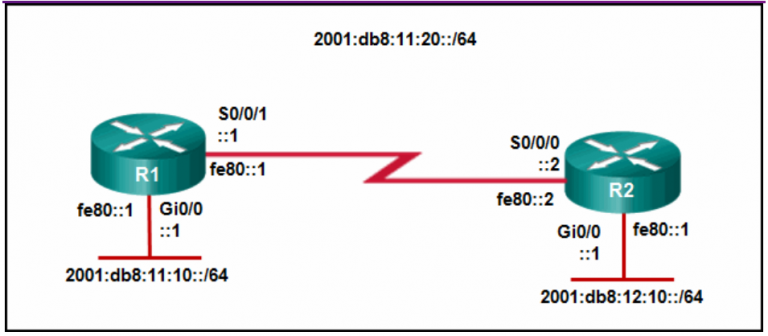
133. Refer to the exhibit. If Host1 were to transfer a file to the server, what layers of the TCP/IP model would be used?
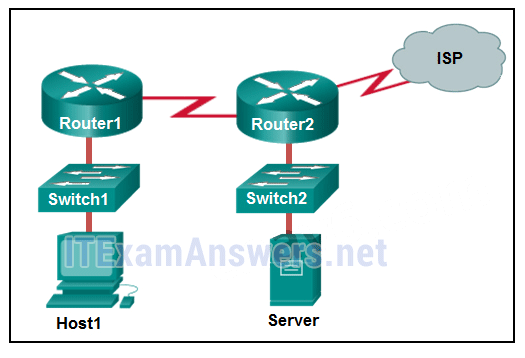
- only application and Internet layers
- only Internet and network access layers
- only application, Internet, and network access layers
- application, transport, Internet, and network access layers
- only application, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
- application, session, transport, network, data link, and physical layers
134. Match the characteristic to the forwarding method. (Not all options are used.)

135. Refer to the exhibit. The IP address of which device interface should be used as the default gateway setting of host H1?

- R1: S0/0/0
- R2: S0/0/1
- R1: G0/0
- R2: S0/0/0
136. What service is provided by Internet Messenger?
- An application that allows real-time chatting among remote users.
- Allows remote access to network devices and servers.
- Resolves domain names, such as cisco.com, into IP addresses.
- Uses encryption to provide secure remote access to network devices and servers.
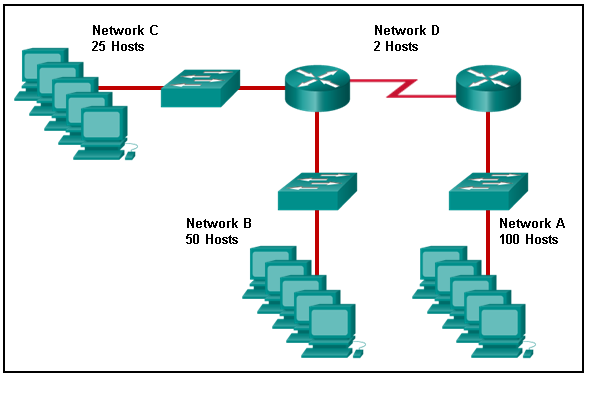
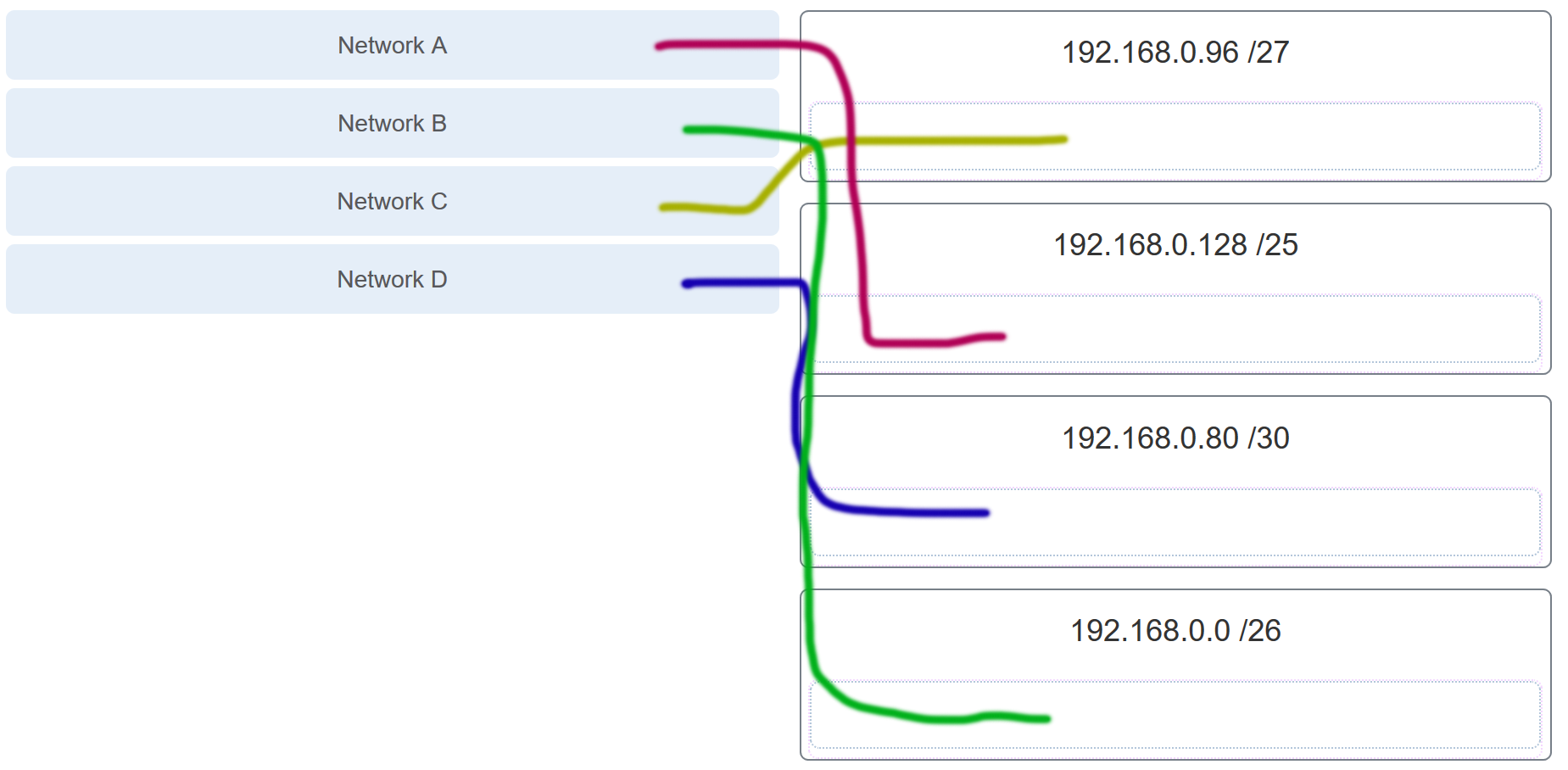
137. Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network.
138. Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol was responsible for building the table that is shown?
interface: 192.168.1.67 — 0xa internet address physical address type 192.168.1.254 64-0f-29-0d-36-91 dynamic . . . interface: 10.82.253.91 —- 0x10
- DHCP
- ARP
- DNS
- ICMP
139. A network administrator notices that some newly installed Ethernet cabling is carrying corrupt and distorted data signals. The new cabling was installed in the ceiling close to fluorescent lights and electrical equipment. Which two factors may interfere with the copper cabling and result in signal distortion and data corruption? (Choose two.)
- crosstalk
- extended length of cabling
- RFI
- EMI
- signal attenuation
140. A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in its ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
- It will send the frame and use its own MAC address as the destination.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
- It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
- It will send a request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.
141. Which two functions are performed at the MAC sublayer of the OSI Data Link Layer to facilitate Ethernet communication?
- integrates Layer 2 flows between 10 Gigabit Ethernet over fiber and 1 Gigabit Ethernet over copper
- enables IPv4 and IPv6 to utilize the same physical medium
- handles communication between upper layer networking software and Ethernet NIC hardware
- adds Ethernet control information to network protocol data
- implements CSMA/CD over legacy shared half-duplex media
142. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 53. What service is the client requesting?
- DNS
- NetBIOS (NetBT)
- POP3
- IMAP
143. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 25 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
255.255.255.128
255.255.255.192
255.255.255.224
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.128
255.255.255.192
255.255.255.224
255.255.255.240
144. What characteristic describes a Trojan horse?
- malicious software or code running on an end device
- an attack that slows or crashes a device or network service
- the use of stolen credentials to access private data
- a network device that filters access and traffic coming into a network
Comments
Post a Comment